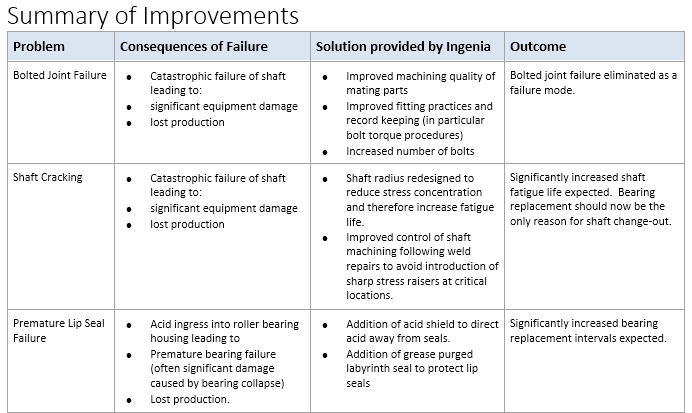
Project Scope
For this project, improvements needed to be made to increase the reliability of acid rollers in a wool processing plant.
Our client had been suffering serious failures of their squeeze rollers in the acidification stage of their carbonising plant. The function of the squeeze rollers is to squeeze moisture out from the wool during the cleaning process. Due to the high rate of stress corrosion cracking in the rollers, the design of the rollers incorporates replaceable stub ends. Despite the stub ends being replaceable, over time, more extensive damage to the rollers has occurred (including seal faces and bearing lands, as well as cracking of shafts). This extra number of replacements and repairs has resulted in the fits and tolerances moving away from acceptable standards which has then further increased the failure rate.
Challenges
Due to the complexity of the project, the Ingenia team used a phased approach to improve the reliability of the acid rollers.
First phase
- To improve the bolted flange connection design in the stub ends, Ingenia’s engineers reviewed the tolerances, fits and bolted connection geometry against those required to meet the need, with many details corrected.
- We assessed the root cause of the unacceptably high failure rate of the bolts. They were suffering fatigue failures due to the combination of poor fit and marginal load capacity. The number of bolts was increased and fits corrected to reduce the actual load on each bolt.
- We also assisted with reviewing the capability of the incumbent repairer which ultimately led to a change of repairer.
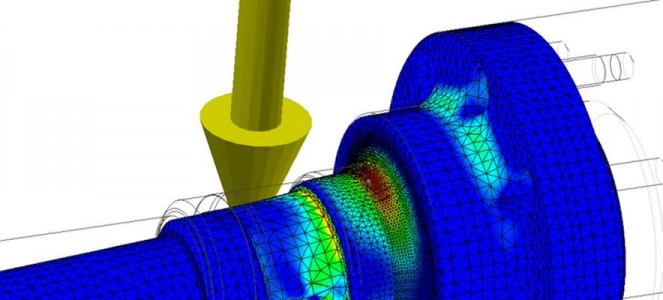
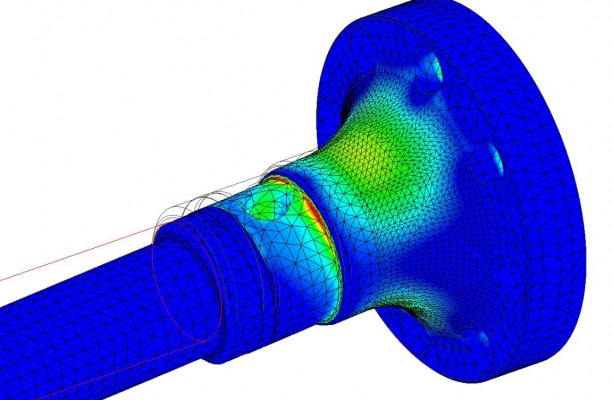
Above: Finite Element Analysis to check stress patterns and levels, with the results of the assessment used to refine the design.
Second phase
- A full repair procedure including Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) was produced for the stub ends (including future weld repairs), which covered when welding is acceptable, how it should be carried out and the quality finish requirements to ensure an “as new” standard for repaired rollers.
- We redesigned the stub end which was snapping at radius diameter transitions. FEA analysis was used to reduce stress concentrations and consequent fatigue risk.
Third phase
- We added a slinger ring to resist acid ingress into the seals and bearing.
- We improved the seal design by adding a labyrinth seal in front of the existing lip seal which, when purged with grease, are expected to have minimal wear and retain the sealing function. (The lip seal alone wears prematurely in the harsh environment and becomes in-effective very quickly.)
Conclusion
The client and Ingenia are expecting an increase in life from only weeks to around 3 years, which has very large operational and maintenance savings. The expected financial benefit of this work is in excess of $150,000 per annum, derived from less outages and reduced maintenance costs.
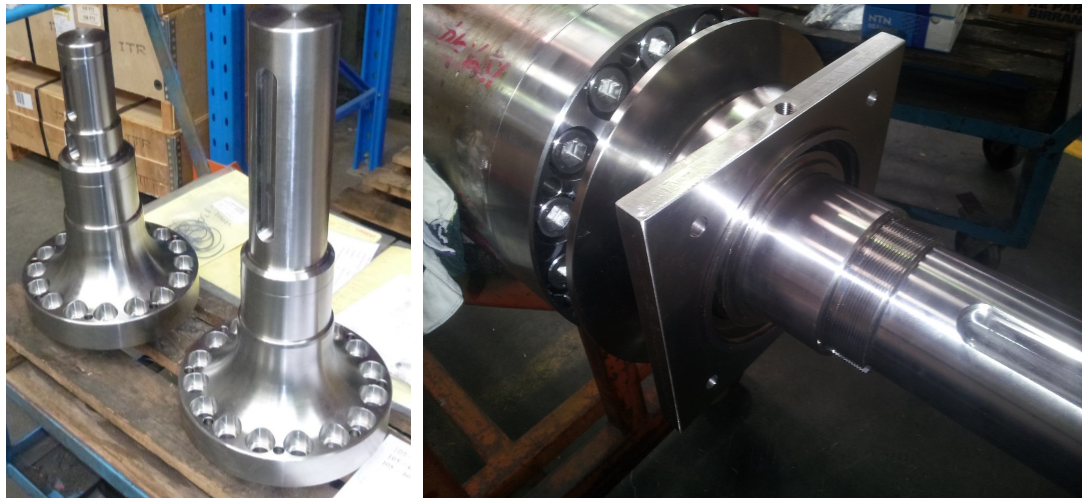
The final machined stub ends: